AI Security Case Study - Bypassing ID.me AI identity Verification - costing $3.4 million.
Bypassing ID.me AI identity verification - costing $3.4 million.
Case Study Number - AISec-0003/24
Summary
An individual in California exploited ID.me's identity verification flaws to file 180 fraudulent unemployment claims, obtaining over $3.4 million by using fake IDs and wigs for false verifications, and was eventually sentenced to nearly seven years for wire fraud and aggravated identity theft.
Threat Capability Level (all levels) – Productionised and Deployed: TRL9
Primary Threat Vector - Bypassing AI Verification
Date – Oct 2020
Reporter – ID.me internal investigation
Actor – One individual
Target - California Employment Development Department
Risk – High Risk
Country – USA
Incident Detail
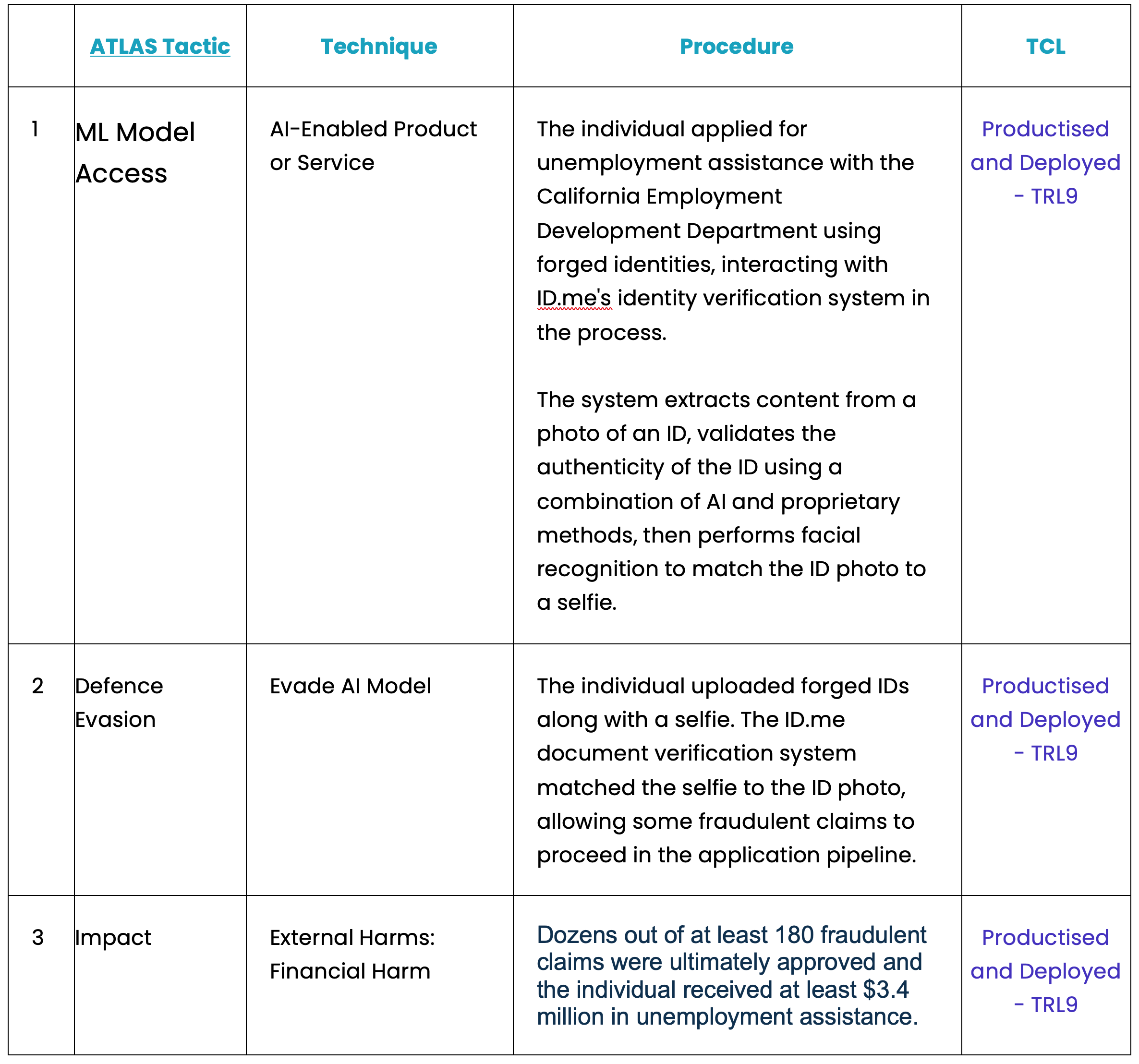
An individual submitted at least 180 fraudulent unemployment claims in California between October 2020 and December 2021 by circumventing the automated identity verification system of ID.me. Dozens of these deceptive claims were approved, resulting in the individual receiving payments totalling at least $3.4 million.
The fraudster amassed several real identities and procured counterfeit driver's licenses with the stolen personal details, complemented by photos of himself wearing different wigs. He then registered accounts on ID.me and completed the identity verification process, which checks personal details and confirms identity by matching the ID photo with a selfie; he successfully verified the stolen identities by wearing corresponding wigs in his selfies.
The claims were filed with the California Employment Development Department (EDD) under these verified identities. Exploiting vulnerabilities in ID.me’s system at the time, the counterfeit licenses were mistakenly approved. Once the claims were accepted, the individual arranged for the payments to be sent to various accessible addresses and subsequently withdrew the funds through ATMs. He managed to extract at least $3.4 million in unemployment benefits. The irregularities were eventually detected by EDD and ID.me, who reported the matter to federal authorities. In May 2023, the individual was sentenced to six years and nine months in prison for wire fraud and aggravated identity theft, related to this and another fraud case.
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures
Mitigations
Undertake an AI security assessment (link).
Catalogue your AI infrastructure assets (hardware and software).
Employ a Secure by design methodology for the development of your AI products and services.
Gain a comprehensive understanding of your supply chain and construct your AI Bill of Materials (AIBOM).
Maintain an Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) feed to stay abreast of emerging AI threat vectors.
Autonomously track, prioritise, and document your vulnerabilities – there are too many for humans to do it.
Utilise a quantitative risk management strategy that justifies investment returns of your control measure.
Initiate a consultation call or go to my useful resources for AI Security.
Final Note
Don’t manage your AI cybersecurity, lead it!
Reference
New Jersey Man Indicted in Fraud Scheme to Steal California Unemployment Insurance Benefits
California EDD - How do I verify my identity for California EDD Unemployment Insurance?
How ID.me uses machine vision and AI to extract content and verify the authenticity of ID documents
Other Related Articles
https://network.id.me/wp-content/uploads/Document-Verification-Use-Machine-Vision-and-AI-to-Extract-Content-and-Verify-the-Authenticity-1.pdf